eamli-operator-docs
Keycloak quick start
Keycloak is used to provide centralised IAM for eamli services.
Setup
Prior to installing keycloak, there are a couple of resources that need to be manually generated.
Database
Please review the database section of this guide for details on creating a database
Create a secret within the same namespace as keycloak will be installed into, containing the database user username and password
$ oc -n eamli create secret generic keycloak-db-secret \
--from-literal POSTGRES_USERNAME=keycloak \
--from-literal POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$(oc -n eamli get secret postgres-pguser-keycloak -o jsonpath='{ .data.password }' | base64 -D)
Custom providers
eamli comes with two keycloak provider packages that skin the authentication screens with eamli branding, and provide custom user mapping.
You can download the theme jar here and the custom role mapper here
These providers can then be installed by storing them in the eamli-keycloak-providers ConfigMap
$ oc -n eamli create cm eamli-keycloak-providers \
--from-file eamli_theme.jar=eamli_theme.jar \
--from-file group_id_mapper.jar=group_id_mapper.jar
Keycloak operator
Keycloak provides an operator that you can install from the operator marketplace via the Openshift dashboard (See (https://www.keycloak.org/getting-started/getting-started-operator-kubernetes)[https://www.keycloak.org/getting-started/getting-started-operator-kubernetes])
Start by going to your Openshift “Administrator” dashboard, and navigate to Operators -> OperatorHub.
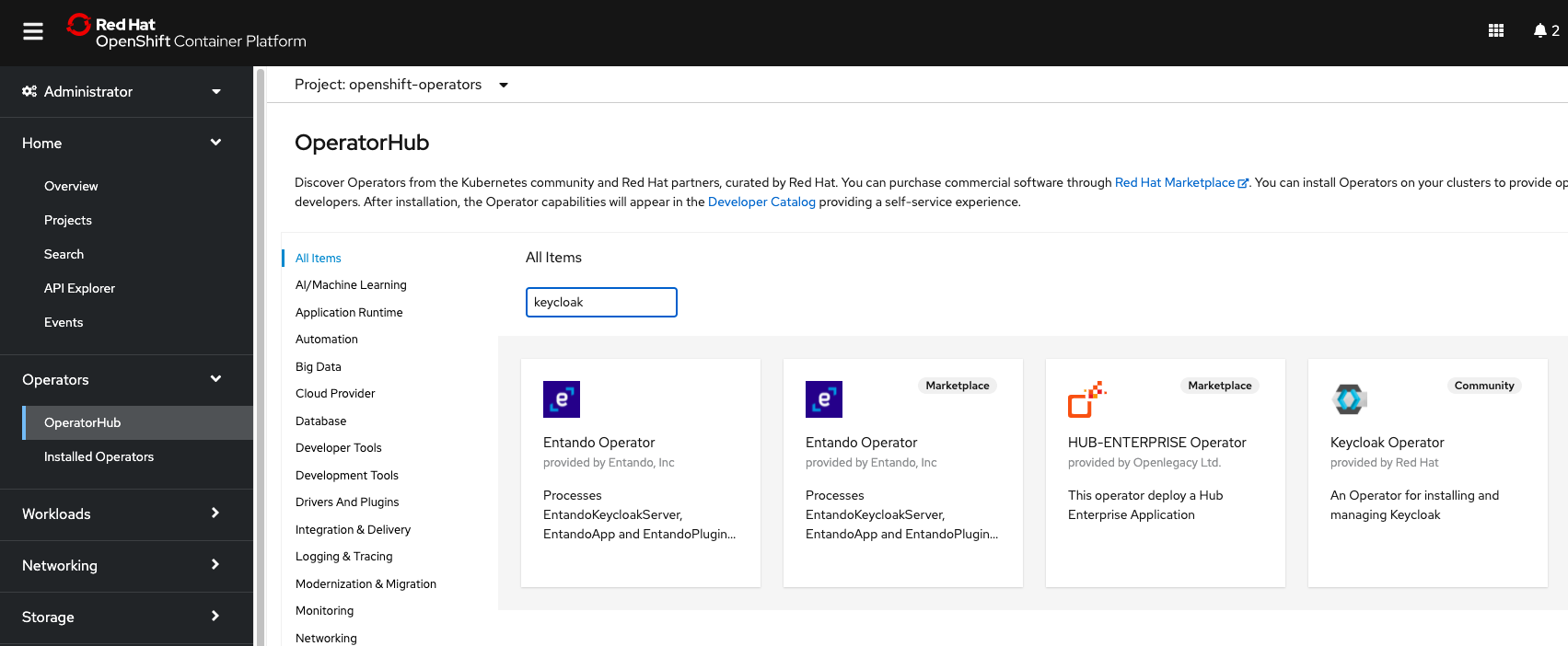
Using the search box type in “keycloak”, select “Keycloak Operator”, and click “Install”.
Select “eamli” for the “Installed Namespace”, and leave everything else as default, and click “Install”.
Now in the Keycloak Operator dashboard, select the “Keycloak” tab, and click “Create Keycloak”. Select “YAML view” and update the YAML with the following, replacing the hostname.hostname value as appropriate:
apiVersion: k8s.keycloak.org/v2alpha1
kind: Keycloak
metadata:
name: keycloak
namespace: eamli
spec:
db:
vendor: postgres
usernameSecret:
name: keycloak-db-secret
key: POSTGRES_USERNAME
passwordSecret:
name: keycloak-db-secret
key: POSTGRES_PASSWORD
host: postgres-primary.eamli.svc
database: keycloak
http:
httpEnabled: true
ingress:
enabled: false
hostname:
strict: false
strictBackchannel: false
hostname: [your domain name]
features:
enabled:
- token_exchange
- admin_fine_grained_authz
additionalOptions:
- name : http-relative-path
value: /auth/
unsupported:
podTemplate:
spec:
containers:
- volumeMounts:
- name: eamli-providers
mountPath: /opt/keycloak/providers
volumes:
- name: eamli-providers
configMap:
name: eamli-keycloak-providers
Ingress is disabled, as it is controlled via the eamli definition Note that the database host (eamli-database.eamli.svc.cluster.local) has not been created at this point, so you might see the pod in a bad state, while waiting for the host to be created by the eamli operator
After a couple of minutes, you should see the pod and service come up
$ oc -n eamli get pods
---
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
keycloak-0 1/1 Running 0 5m22s
keycloak-operator-786bcb4988-grj5g 1/1 Running 0 10m
$ oc -n eamli get service
---
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
keycloak-discovery ClusterIP None <none> 7800/TCP 20d
keycloak-gke ClusterIP 10.30.134.62 <none> 8080/TCP 124d
keycloak-service ClusterIP 10.30.21.212 <none> 8080/TCP 20d
$ oc -n eamli get secrets
---
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
keycloak-db-secret Opaque 2 10m
keycloak-initial-admin kubernetes.io/basic-auth 2 10m
keycloak-secrets-store Opaque 1 10m